Seaweeds, stem cell therapy, and health of liver disease patients
Dr. Ming-Shun Wu
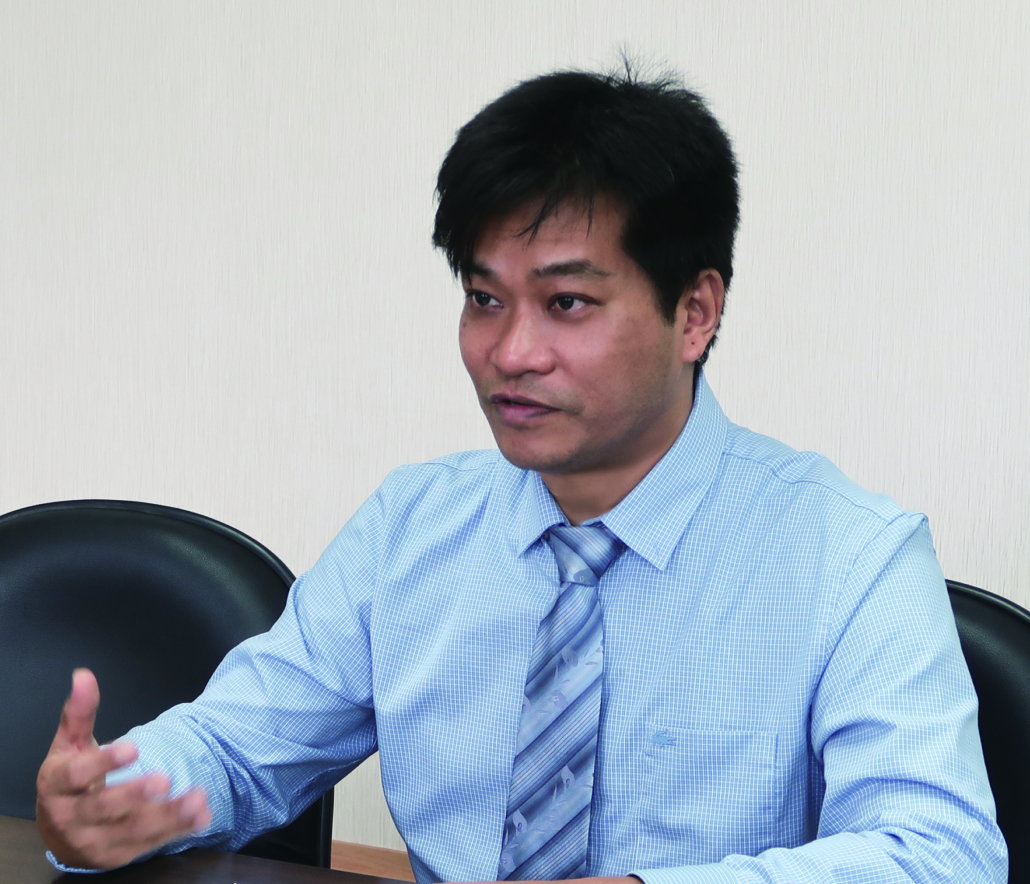

Director, Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Wan Fang Hospital
Assistant professor, School of Medicine, Taipei Medical University
From a medical family, versed in medical traditions from the East and West, and with interests in both basic and clinical research, Dr. Ming-Shun Wu draws on a broad range of knowledge in medical research and practical expertise for the good of his patients.
“I followed him into the mountains to take some herbal medicines. He also taught me to palpate pulse, to do acupuncture.”
Dr. Ming-Shun Wu began his interest in medicine from childhood. When accompanying his grandfather, he learned how to use Chinese herbs and traditional techniques. He later brought his interest in healing to TMU, where he earned his MD and PhD in clinical medicine, filed licenses in both Chinese and Western medicine, and has served at Wanfang Hospital for the past 26 years. Director of TMU’s Department of Gastroenterology since 2015, he also teaches at the TMU Center for Cell Therapy and Regeneration Medicine. His eclectic background is reflected in a broad range of research interests that span Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) diagnosis and treatments, clinical research on components of herbal remedies, and stem cell therapy for cancer treatment.
Focoidan, Fucoxanthin, and Fatty Liver Disease
“The function of seaweed in Chinese medicine is to lose weight and reduce tumors.”
Brown seaweed has been used in traditional herbal medicine for weight loss and tumor reduction. More recently, studies have shown beneficial effects stemming from two of the plant’s compounds; fucoidan fights viruses, inflammation, and tumors, while fucoxanthin acts as a potent antioxidant that can modulate inflammation and cancer.
Although eating one would be healthy, you probably can’t get all the benefits of fucoidan and fucoxanthin from a seaweed salad. According to Dr. Wu, the concentrations are too low, and absorption may not be ideal. These problems are something that HiQ Marine Biotech wants to address with a patented brown seaweed supplement.
The company contacted TMU’s Office of Business Development to conduct a study of their product, and a background in Western and Chinese medicine, clinical and research expertise, and access to patients at Wanfang Hospital placed Dr. Wu perfectly to look into HiQ Marine Biotech’s product.
In a double-blind study of sufferers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, patients were given a regimen of brown seaweed supplement or placebo. Evaluated at one and three months, patients in the treatment group showed increasing improvements in blood markers for liver. Physical changes to their livers took a bit more time, but decreased liver fattiness was seen by month six.
According to Dr. Wu, NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) may potentially lead to problems such as cirrhosis and cancer, and there is little certainty regarding existing pharmacological interventions. So for patients who are less able to make lifestyle changes because of disability supplementation looks like a good option. And because chronic inflammation of the liver can induce cancer, further investigations into how the underlying mechanisms of fucoidan and fucoxanthin reduce inflammation are planned.
New Opportunities in Stem Cell Therapy
As governmental regulations loosen, Dr. Wu also plans to work with companies to develop stem cell products to treat patients with liver cirrhosis and stage 4 cancer. Dr. Wu is hopeful about this newly opening avenue of research. In a yet to be published case study, he reports preliminary success using stem cells to extend the life of a stage 4 cancer patient by 11 months.
From cutting edge stem cell treatments to basic cancer research to improving health outcomes through TCM-informed nutritional supplements, Dr. Ming-Shun Wu’s work embodies a most effective melding of Eastern and Western traditions. You can hear his perspective first-hand in TMU’s International Master’s or PhD Program in Cell Therapy and Regeneration Medicine.
For interviews or a copy of the paper, contact Office of Global Engagement via global.initiatives@tmu.edu.tw.