Urologist gives treatment advice for enlarged prostates
Source: Taipei Medical University
Published on 2019-01-08
You may have an enlarged prostate gland if you are a man and have slow and interrupted urination, difficulty urinating despite feeling of fullness, use of abdominal muscles when urinating, repeated or frequent night trips to urinate, or uncertain bladder control.
In a urology consultation, the doctor will arrange tests to determine if your issues are caused by an enlarged prostate. If so, this can be improved through changing your lifestyle, consistent follow-ups, and/or medical treatment or surgery to improve quality of life. When symptoms are minor, consistent follow-up and lifestyle changes such as drinking water at the right time, eating the correct diet and exercising can possibly improve the condition.
In terms of medical treatment, the main drugs used are alpha-blockers that help the bladder relax the urethra to reduce blockage at the sphincter and make urination easier. However, one should be cautious in the early stages of medical treatment when changing positions to prevent postural blood pressure problems.
If the prostate enlargement is moderate to severe and prostate cancer has been ruled out, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can be taken to suppress further prostate enlargement. Patients must be mentally prepared for a long-term effort because prostate enlargement is a chronic disease, and drugs can control symptoms but not eliminate them.

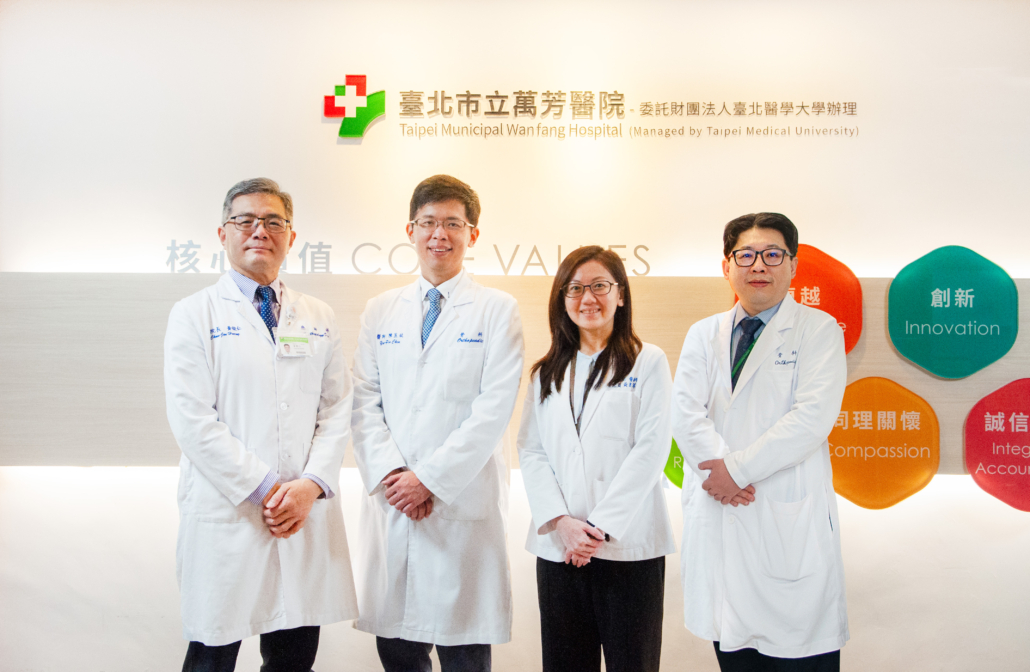
Dr. Hung-Jen Shih of Taipei Municipal Wanfang Hospital’s urology department.
When results of medical treatment are poor or drugs produce side-effects, or in cases with other complications, surgery can be considered. With advancements in medical techniques and equipment, traditional open surgeries have yielded to micro-level techniques and endoscopic surgeries. Currently endoscopic mono/bipolar TURP and laser prostatectomy are favored approaches.
The laser option can significantly reduce bleeding and water intoxication during surgery, and patients are less likely to suffer from urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction. This is suitable for treating elders with high blood pressure, or chronic disease patients with heart disease or diabetes. These patients must continue to follow physicians’ advice in terms of lifestyle and diet after surgery.